Advantages of Blow Molding Compared to Rotational Molding:
- Cost-Effectiveness for High Volume:
- Blow molding is generally more cost-effective for producing large quantities of products due to shorter cycle times and lower per-unit costs once high initial tooling costs are covered. According to information on the web, blow molding can produce parts at a rate of about 70 parts per hour compared to rotational molding’s 1-2 parts per hour for similar size products.
- Design Flexibility for Simple Shapes:
- Blow molding excels in creating hollow, thin-walled parts with simpler geometries like bottles and containers. The process allows for intricate contours, handles, and indentations which can be difficult with rotational molding.
- Faster Production:
- The cycle time in blow molding is significantly shorter, allowing for rapid production rates. For example, a 2000L tank can take 8-9 pieces per hour with blow molding, while rotational molding might only produce 1-2.
- Material Efficiency:
- Blow molding uses less material due to its direct process of expanding a parison into the mold shape, reducing waste.
- Precision in Wall Thickness:
- Blow molding can control wall thickness more precisely with electronic parison programmers, providing strength where needed.
- Mold Durability:
- Blow molds tend to last longer than rotational molds, which might need replacement after 3,000 cycles.
Disadvantages of Blow Molding Compared to Rotational Molding:
- High Initial Tooling Costs:
- The upfront cost for blow molding molds is high, making it less suitable for low-volume production or prototyping where rotational molding’s lower tooling costs are advantageous.
- Limited Design Complexity:
- Complex shapes or parts with significant undercuts are challenging or impossible with blow molding. Rotational molding allows for more complex geometries, including double walls and detailed surface finishes without seams or weld lines.
- Wall Thickness Control:
- Although blow molding can control wall thickness, it still might not match the uniform wall thickness that rotational molding can achieve, especially in critical areas.
- Material Limitations:
- Blow molding primarily uses thermoplastics like HDPE, but options are somewhat limited compared to rotational molding, which can use various poly-based resins in powder form, albeit more costly.
- Precision and Detail:
- Blow molding might have lower precision for intricate details compared to injection molding or even rotational molding in some cases, particularly for complex parts.
- Environmental Impact:
- Blow molding relies heavily on petroleum-based plastics, contributing to environmental concerns, although this is somewhat mitigated by the ability to recycle materials within the process.
- Automation vs. Manual Labor:
- While blow molding can be highly automated, reducing labor costs, rotational molding often requires more manual intervention, but its process simplicity can be advantageous for smaller-scale or artisanal production.
Blow molding is best for high-volume production of simpler, hollow products where speed and cost per unit are critical, while rotational molding suits lower volumes or when design complexity and uniform wall thickness are priorities. Sources like Fictiv, Xometry, Roto Dynamics, and Yankang Plastic Machinery provide insights into these comparisons, emphasizing the need to match the manufacturing process to the specific requirements of the product.
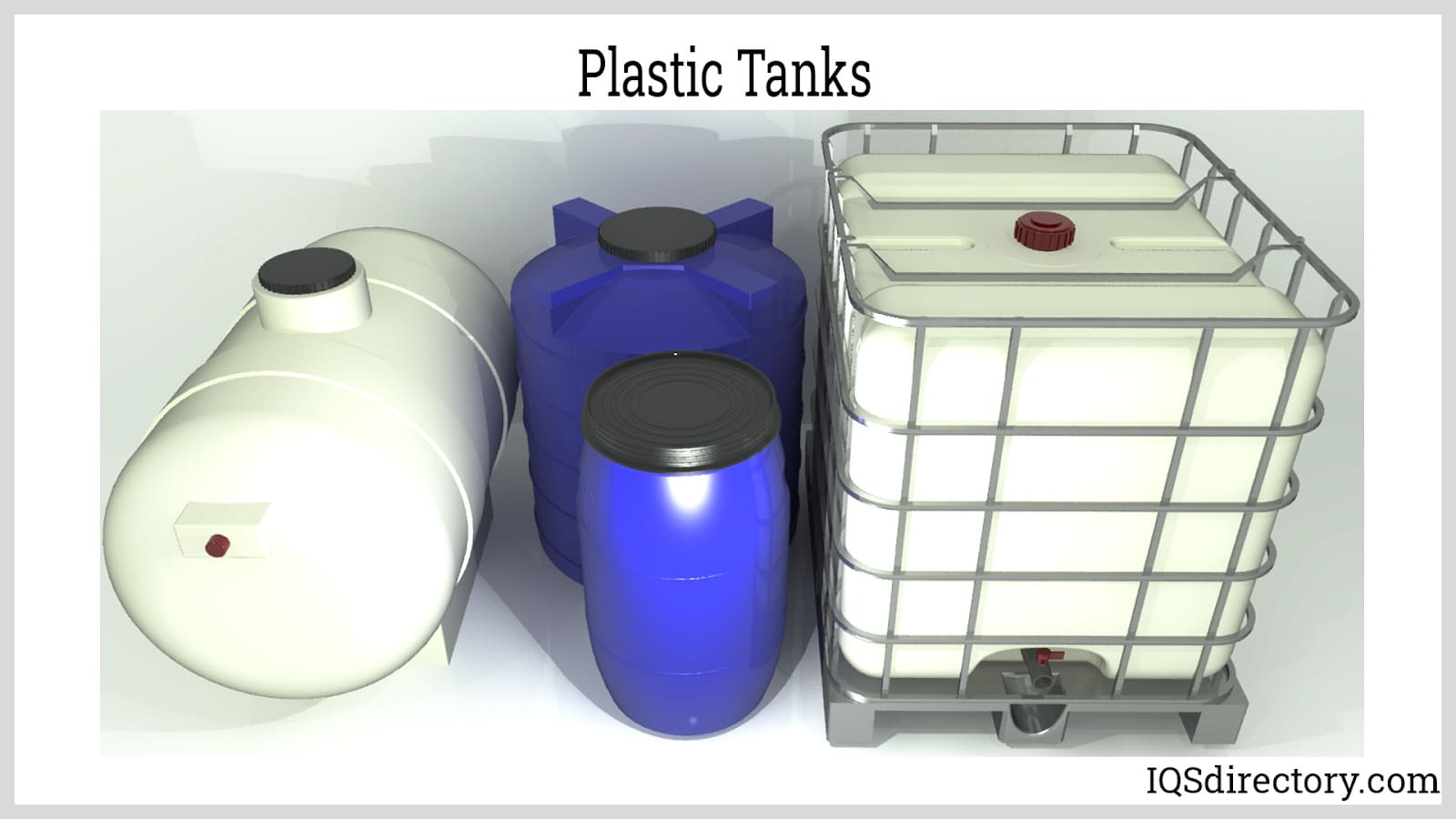





 Fiberglass Fabricators
Fiberglass Fabricators Injection Molded Plastics
Injection Molded Plastics Plastic Blow Molding
Plastic Blow Molding Plastic Dip Molding
Plastic Dip Molding Plastic Extrusions
Plastic Extrusions Plastic Tubing
Plastic Tubing Polyurethane Molding
Polyurethane Molding Rotational Molding
Rotational Molding Vacuum Forming
Vacuum Forming Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services